
But duplicate factors are only counted once, so one only has one factor.

The only way to get a product of one is by multiplying 1 x 1. A composite number must have a finite number of factors. Since any number times zero equals zero, there are an infinite number of factors for a product of zero. All even numbers (except the number two) are composite, since they can all be divided by two. This is one of the remaining big math mysteries out there for mathematicians.Ĭomposite numbers have more than two factors but not an infinite number of factors. There is no pattern for finding all of the prime numbers that exist, although mathematicians have found prime numbers with almost eight million digits. If you know your divisibility rules (covered in the next section), then determining the prime numbers from 1–100 is a relatively easy task. Prime numbers have exactly two factors, one and the number itself.
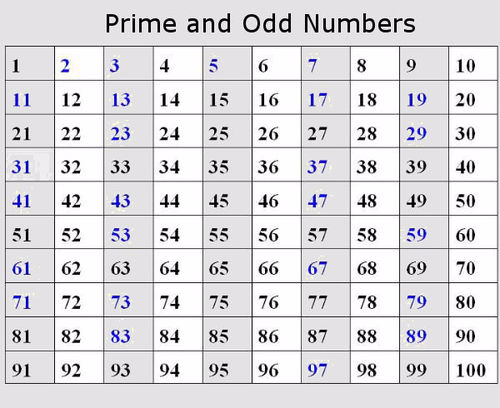
Let’s take a look at the difference between prime and composite numbers.
So far, we’ve covered the various types of numbers (real numbers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, whole numbers, and integers), as well as how they relate to each other using the common device of a number line.We’ll also review some handy rules that make division faster and easier. In this lesson we will review prime and composite numbers. ⬅ Previous Lesson Workshop Index Next Lesson ➡


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
